使用片段主成分分析策略的抗菌元胜肽的定量序效模型:一种描述和预测肽药物(含有L/D和非自然残留)的方法
Published: 2016-01-27
Keyword: Cell-Penetrating Peptides,多肽修饰,抗菌肽
关键词:阳离子抗菌肽,超级病毒,定量序效
出版时间:: 2015-10 Amino Acids (2015) 47:125-134
由多重药物抑制细菌和真菌感染处理尤其是个挑战,阳离子抗菌肽(CAPs)被认为是具有前景的药物替代品用于治疗超级病毒。随着抗蛋白酶的生物利用度和稳定性的增多,现在的研究已经集中设计这些肽上面。
在该研究中,来源于O-W-F-I-F-H(1-Bzl)-NH2 序列的60个抗菌肽的定量序效模型(QSAM),其显示了卓越的广谱抗危险微生物的活性,如MRSA、MRSE、大肠杆菌和白色念珠菌。肽含有两个同分异构体 D和L的天然和非天然的氨基酸(AAs)。通过片段主成分分析策略研究氨基酸的结构描述符以提取氨基酸的索引。结果表明构建的模型涵盖了MRSA、MRSE、大肠杆菌和白色念珠菌数据集中82、94、80和78%的交互验证变异数。结果也被用于测定重要和显著的氨基酸(其在抗菌肽活性具有重要性)。
该研究主要的发现是首次在肽(含有两个同分异构体 D和L的天然和非天然的氨基酸)的定量序效模型研究中首次成功尝试。
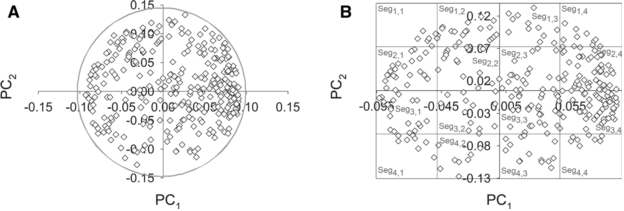
a Distribution of the calculated descriptors for amino acids in the 2D-space of the first and second PCs in the descriptors’ direction (loading 1 and loading 2). b Partitioning of the descriptors into 16 segments by vertical and horizontal lines to extract amino acid indices
a:在描述符方向(载荷 1 和载荷 2)的第一和第二主成分(PCs)二维空间中氨基酸计算的描述符分布图;b: 通过垂直和水平线将描述符分割成16个部分以提取氨基酸索引
Keywords Cationic antimicrobial peptides, Superbugs, Quantitative sequence-activity
modeling · Amino acid descriptors
Published time: 2015-10 Amino Acids (2015) 47:125-134
The treatment of infections caused by multidrugs resistant bacteria and fungi is a particular challenge. Whereas cationic antimicrobial peptides (CAPs) are considered as promising drug candidates for treatment of such superbugs, recent studies have focused on design of those peptides with increased bioavailability and stability against proteases.
In this study, the quantitative sequence-activity modeling (QSAM) of 60 CAPs derived from O-W-F-I-F-H(1-Bzl)-NH2 sequence which showed excellent activities against a broad range of hazardous microorganisms: e.g., MRSA, MRSE, E. coli and C. albicans, is discussed. The peptides contained natural and non- natural amino acids (AAs) of the both isomers D and L. A segmented principal component strategy was performed on the structural descriptors of AAs to extract AA’s indices. Our results showed that constructed models covered more than 82, 94, 80 and 78 % of the cross-validated variance of C. albicans, MRSA, MRSE and E. coli data sets, respectively. The results were also used to determine the important and significant AAs which are important in CAPs activities.
The main finding of this study is that it is the first successful attempt in the QSAM studies of peptides containing both natural and non-natural AAs of the both L and D isomers.



 关注我们
关注我们

